Here are a few terms that are frequently used when we talk about AC, that is, Alternating Current. Some of them are used when talking about Direct Current as well.
Introduction

In some of the other articles, we have read about current electricity. There is also static electricity. Here, we will read about the type of electricity that we call alternating current, or simply AC.
The alternative to AC is DC, or Direct Current. In DC, the current flows in only one direction — from the positive to the negative terminal of a battery, cell, or DC generator. DC can also be generated using a solar photovoltaic cell. Coming back to AC, as the term says, current is alternating. It means that direction of flow of current alternates.
If we plot the graph of current flowing through a circuit with an AC source, it is in the shape of a wave. This wave is called sinusoidal wave, or sine wave, in short.
In AC, both the current and the voltage rise and fall in the form of a sine wave. The positive part is upper part of the wave, while negative voltage or current is in the lower part.
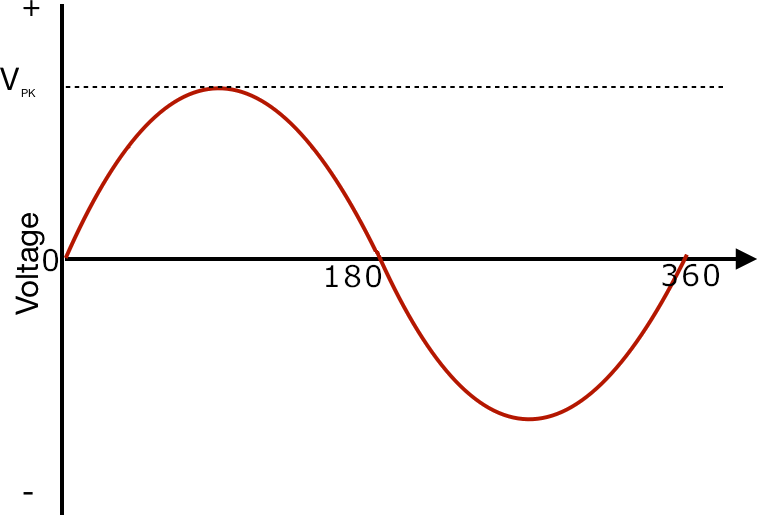
Some AC Terms
Cycle: It means one complete wave from 0o to 360o. A half cycle is from 0o to 180o. In radians, 180o is π and 360o is 2π
Period (T): It is the time taken for one complete cycle. It is measured in seconds (s).
Frequency (f): The number of cycles in one second is called the frequency of the wave. It is measured in hertz (Hz). The frequency of power in India is 50 Hz. It means that there are 50 cycles of voltage and current in each second. Frequency of power in USA is 60 Hz.
Peak/Maximum/Amplitude (Vm): It is the highest value attained by the wave in positive or negative direction.
Peak to Peak (Vpp): It is the distance between the maximum positive and maximum negative values.
Average value: It is the mean or average of the AC wave taking both the positive and negative values. Since both positive and negative values are equal, average value of a full cycle sine wave AC is zero.
How is AC voltage or current measured?
Current and voltage change continuously in AC unlike DC which is steady and straightforward. To accurately measure these fluctuating AC values, we use the RMS (Root Mean Square) method.
The RMS value allows us to compare AC with DC by focusing on the heat produced. For a given period, a certain value of DC current produces a specific amount of heat in a conductor. The RMS value of AC is the amount of AC current that produces the same heat over the same time. This comparison helps standardize AC measurements for practical and engineering applications.
AC voltmeters (voltage measuring devices) and ammeters (current measuring devices) give the respective readings in RMS values. All the values that we talk about with respect to AC are in RMS values. When we say the voltage supply to our house is 220 V, we are referring to the RMS value of the voltage.
The relation between RMS value and the maximum value
The RMS value of AC is approximately 70.7% of its peak value. To be more accurate, the relation between VRMS and Vm is
VRMS=Vm/√2 or 0.707 Vm
The RMS reading of an AC voltmeter is 220 V. So its maximum or peak value is √2 times 220, or 311.12 V. The actual instantaneous value of the AC voltage is far higher than what is shown by the meter.
Types of AC
There are two variations in AC – Single phase and multiphase. Multiphase means more than one phase. It can be 2 phase, 3 phase, 6 phase, 12 phase. Most common multiphase system is the three phase AC. The other multiphase systems have some special usages which are not commonly used. So we usually limit AC systems to single phase and three phase AC.
Single phase AC: There is a single sine wave of AC current and voltage. AC power travels through two wires, called the phase and the neutral. Almost all the electrical devices we use at our homes are single phase devices. They are called single phase loads and are connected to the supply through these two wires.
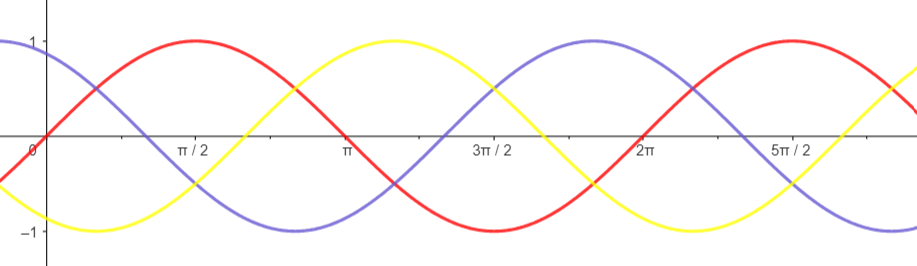
Three phase AC: There are three sine waves that are 120o apart. They are called red, yellow, blue phases, or RYB in short. Three phase AC systems have four wires – three for the R, Y, B phases, and one neutral wire.
Three phase wiring carries more voltage and power compared to single phase. So, large generating stations with AC generators (also called Alternators) are always wired in 3 phase.
How are three phase and single phase related to each other?
Three phase wiring is in two types – Star and Delta.
Star wiring is also called Wye wiring, as it resembles the letter Y. It has four lines, that is, Red, Blue, Yellow, and the Neutral. Delta wiring has only R. B. Y lines, and no neutral.
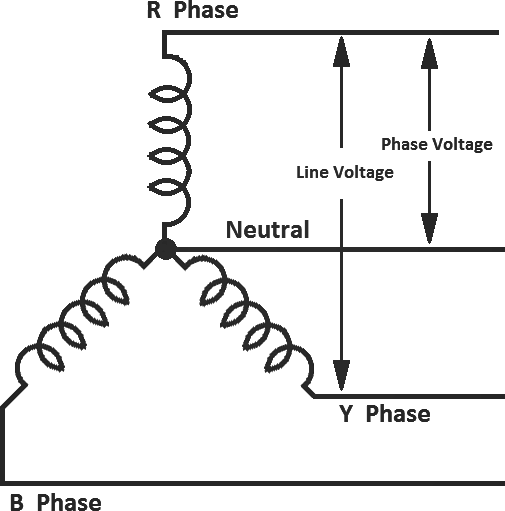

The voltage between any two phases is called Line Voltage, VL (or line to line voltage). The voltage between any one of the phases and the neutral is called Phase Voltage, VP (or line to neutral voltage).
Alternators have star wiring. Therefore, four wires emerge out of generating stations. To obtain single phase power, one of the phase wire and the neutral are tapped. This means that single phase voltage is the phase voltage. The relation between line voltage and phase voltage in a star wiring is:
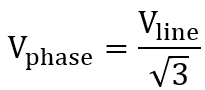
So if the single phase voltage measured is 230 V, it means the the 3 phase voltage generated by the alternator is approximately 400 V.
In a delta connection, line voltage and phase voltage are the same.
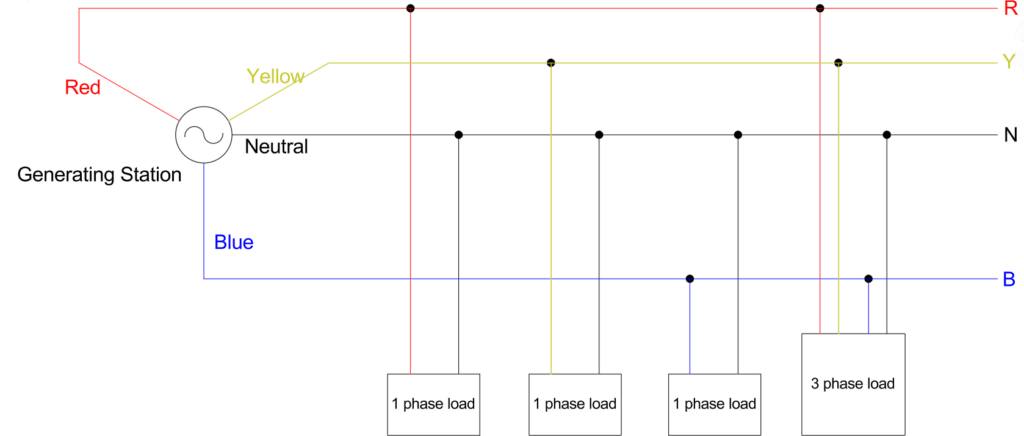
Single phase loads are tapped between neutral and any one of the phases. Three phase loads are tapped from all the four lines.
Three phase loads are those devices or systems that require higher power when compared to single phase loads.
Power in a three phase circuit
Irrespective of whether the 3 phase AC wiring is star or delta, the power is given by
Here, both V and I are line voltage (VL) and line current (IL).
cosø is called the “power factor” of the circuit. It is a very important parameter in AC circuits, which is covered in another opic.
We will see the components of AC circuits in other articles.


I appreciate, cause I found exactly what I was looking for. You have ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
My spouse and i were absolutely happy that Emmanuel managed to complete his investigations from your ideas he got when using the site. It’s not at all simplistic just to find yourself giving away instructions that a number of people might have been making money from. And we all discover we have got the blog owner to thank for this. These explanations you’ve made, the simple blog navigation, the friendships you assist to foster – it is many astonishing, and it is letting our son and us understand this concept is cool, and that is highly vital. Many thanks for everything!
I think the article is incomplete as of now. Please complete it
Good writing
Written in a simple manner. Waiting for next series on this topic
Very good